- Company
- Industries
- Product areas
- Innovation
- Jobs and Career
- Apprenticeship
- News

Clad materials are metallic composite materials. In these materials, two or more metals are bonded together, primarily by roll bonding.
The use of such materials is widespread. They are used for decorative products, electrical applications and mechanically stressed parts in corrosive environments.
Miba combines roll bonding with the advantages of strip casting specific bearing materials. This results in precisely tailored and economical products for highly stressed applications.
The clad materials produced by Miba in this way are used as starting materials in bearing manufacturing. Miba supports its customers with comprehensive materials and engineering expertise, from product design to industrial series production.
What is roll bonding? What advantages does it offer compared to other processes? How can strip casting of bearing materials be effectively integrated into the process chain? We answer these questions in this article.

Roll bonding is a process for joining different metals together using mechanical rolling pressure, without any welding or soldering.
The process works as follows:
The quality of the bond depends largely on the surface preparation: Before roll bonding, the materials are cleaned and then mechanically treated by brushing or grinding.
This serves to remove surface contaminants and to bring the surfaces into an “active” state, i.e., one that is capable of bonding.
The process enables the combination of carrier and functional materials, for example a steel base body with an aluminum layer. Precise process control allows the production of a stable and materially coherent composite material with precisely adjustable layer thicknesses. The special properties resulting from the combination of different materials can thus be ideally tailored to applications with specific requirements:
• Mechanical and corrosive resistance
• Special electrical properties
• High thermal conductivity
• Good tribological properties
Clad materials are used wherever functional surface properties need to be combined with high mechanical stability. The composite material allows targeted adaptation to tribological, electrical or chemical requirements while ensuring efficient use of materials.
Typical areas of application are:
The ability to bond different metals and their properties on metallurgical level opens up great design freedom and material efficiency for clad materials.

Roll bonding offers decisive advantages over conventional joining methods such as welding or soldering. This is particularly the case when it comes to the production of large-area composite materials.
The most important advantages include:
In contrast to thermal or chemical processes, the bond formed during roll bonding is purely mechanical. This means that no intermetallic phases form at the interface. The heat-affected zone, which is undesirable but unavoidable in welding, does not occur in this process either. The material bond is solid, durable and free of additional materials.
Compared to other cladding processes such as explosive cladding, roll cladding is a reliable, process-secure and cost-efficient solution. This is particularly true in combination with a coordinated casting process such as strip casting.
Miba offers in-depth manufacturing expertise for a wide range of industrial applications and products.

In continuous casting, liquid metal is cast directly into a thin, endless strip. This eliminates the need for large semi-finished products/slabs and subsequent heavy rolling.
Miba relies on the proven belt caster process for the energy-efficient and material-saving production of continuous bearing alloy strips with a defined microstructure.
The cast alloy strip offers several advantages in downstream roll cladding:
Strip casting enables the production of high-precision clad strips for clad materials. This is particularly the case with materials such as aluminum alloys, which Miba processes. The combination of strip casting and roll bonding forms a continuous process chain. It offers both technical and economic advantages.
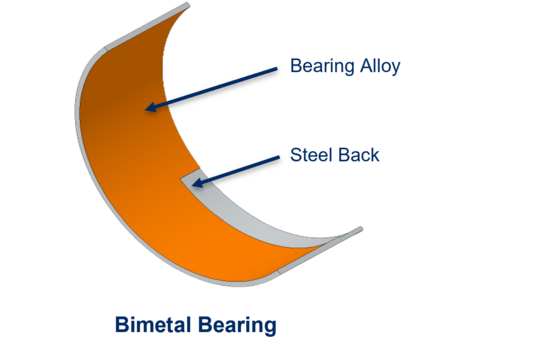
The production of clad materials is based on an efficient process chain in which casting, cladding and further processing are optimally coordinated:
Miba uses both standard and special alloys to meet different physical, tribological or thermal customer requirements.
Typical material combinations are:
Miba supports you with its materials and engineering expertise, as well as its many years of application and simulation experience. Talk to our experts. Together, we will find the right solution for your requirements.
Our blog offers in-depth insights, practical tips and the latest technological innovations. Stay up to date with expert knowledge, exciting developments and valuable industry insights!